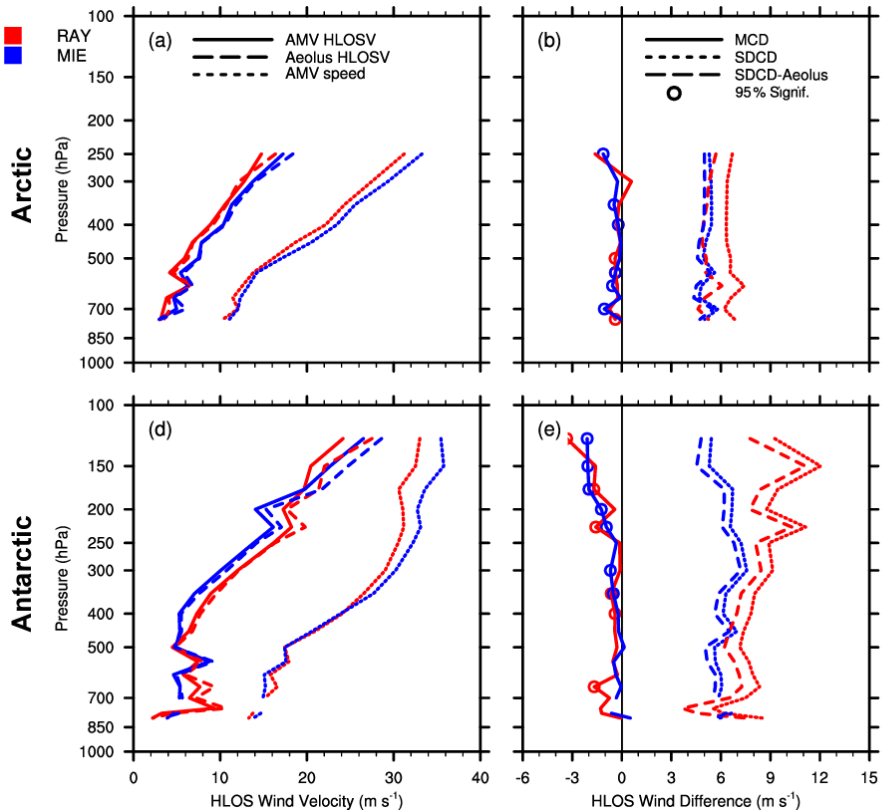
ESSIC/CISESS Scientists Katherine Lukens (a former CISESS grad student), Kayo Ide, Hui Liu, and Ross Hoffman have a new article in the journal Atmospheric Measurement Techniques about their work with the NOAA/NESDIS Office of Projects, Planning, and Acquisition (OPPA) Technology Maturation Program (TMP). The need for highly accurate atmospheric wind observations is a high priority in the science community, particularly for numerical weather prediction (NWP). To address this need, this study leverages Aeolus wind lidar level-2B data provided by the European Space Agency (ESA) as a potential comparison standard to better characterize atmospheric motion vector (AMV) bias and uncertainty.